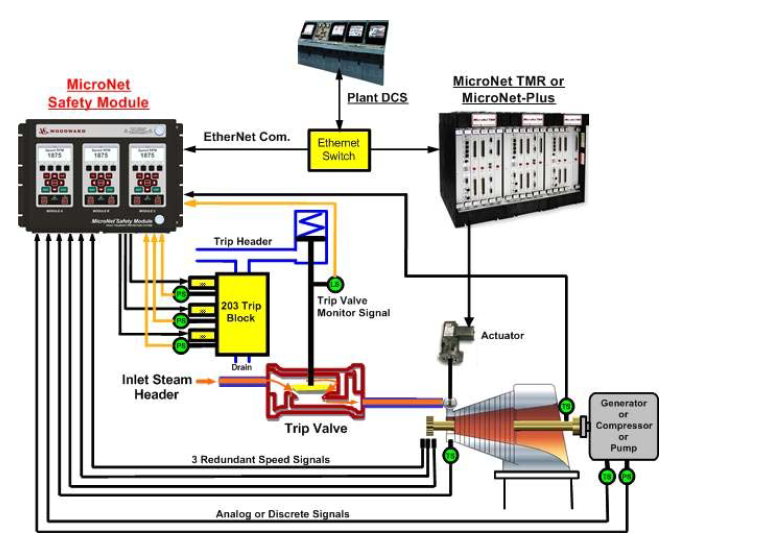
Smart I/O modules.
During initialization of a smart module, the module’s microcontroller turns the LED off after power-on self-
tests have passed and the CPU has initialized the module. The LED is illuminated to indicate an I/O fault.
The CPU also tells this module in which rate group each channel is to run, as well as any special
information (such as the type of thermocouple in the case of a thermocouple module). At run time, the
CPU then periodically broadcasts a “key” to all I/O cards, telling them which rate groups are to be
updated at that time. Through this initialization/key broadcast system, each I/O module handles its own
rate-group scheduling with minimal CPU intervention.
These smart I/O modules also have on-card on-line fault detection and automatic
calibration/compensation. Each input channel has its own precision voltage reference. Once per minute,
while not reading inputs, the on-board microcontroller reads this reference. The microcontroller then uses
this data read from the voltage reference for both fault detection and automatic temperature
compensation/calibration.
Limits have been set for the expected readings when the on-board microcontroller reads each voltage
reference. If the reading obtained is outside these limits, the system determines that the input channel,
A/D converter, or the channel’s precision-voltage reference is not functioning properly. If this happens, the
microcontroller flags that channel as having a fault condition. The CPU will then take whatever action the
application engineer has provided for in the application program.
A smart output module monitors the output voltage or current of each channel and alerts the system if a
fault is detected.
Each I/O module has a fuse on it. This fuse is visible and can be changed through a cutout in the plastic
cover of the module. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the same type and size.









Đánh giá
Chưa có đánh giá nào.